Log Expensive Queries Into Files By Extended Events
04 Sep 2021 | MSSQLIn the previous blog, we discussed how to print slower SQLs and print them at the console in real-time. But it is inconvenient because DBA may tiredly execute the same printing snippet many times over, which causes drama. Let’s dwell on this occasion, that you need to watch all the expensive queries run in the middle of the night, and you are not available to execute the printing snippet.(Even though sys.dm_exec_query_stats caches query plans, but it is still possible to release cached plans when it is less valuable.)
So, You need a mechanism, which can periodically scan slower SQLs, or instantly write down expensive SQLs into log files. Fortunately, SQL Server provides a functionality called Extended Events. You can measure SQL’s running time once it finished its query, and that is awesome. All that you need to do is to register an event, and SQL Server will do these dirty boring jobs for you automatically. For more Extended Events details, Take a look at Microsoft’s Extended events overview.
The following guidance will illustrate you to set up an expensive SQL query’s logging configuration. As I mentioned early, SQL Server provided Extended Events, which are easy and convenient to use. There are several ways that you can create an Extended Event through a T-SQL snippet, “New Session” on SSMS, or “New Session Wizard” on SSMS.
I will only represent the first method of creating an Extended Event by using a T-SQL snippet. This blog doesn’t discuss the other two, as it is out of this article’s scope. Actually, “New Session” and “New Session Wizard” can be easily complete through SSMS’s UI. If you are interesting, take a look at Quickstart: Extended events in SQL Server.
USE MASTER;
GO
/* Conditionally drop the session if it already exists */
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.server_event_sessions WHERE name = 'EE_ExpensiveQueries')
DROP EVENT SESSION EE_SlowQueryLog ON SERVER;
GO
/* Create the session */
CREATE EVENT SESSION EE_ExpensiveQueries
ON SERVER
ADD EVENT sqlserver.sql_statement_completed
(
ACTION (sqlserver.sql_text)
WHERE cpu_time > 500 /*total ms of CPU time*/
)
ADD TARGET package0.asynchronous_file_target
(SET
FILENAME = N'C:\SQLskills\EE_ExpensiveQueries.xel',
METADATAFILE = N'C:\SQLskills\EE_ExpensiveQueries.xem'
)WITH (
MAX_DISPATCH_LATENCY = 1 seconds
);
GO
/* Start Session */
ALTER EVENT SESSION EE_ExpensiveQueries ON SERVER STATE = START;
GO
Once you create and start the above session, you will see SQL queries that spent more than 500 milliseconds will be logged under the C:\SQLskills\ folder.
Now, Our event captured expensive queries. The next step is to present captured slow records. You can do that by opening Management->Extended Events->Sessions On SSMS, opening log’s files with SSMS application, or query the logs in SQL.
Opening Management->Extended Events->Sessions Menu On SSMS:
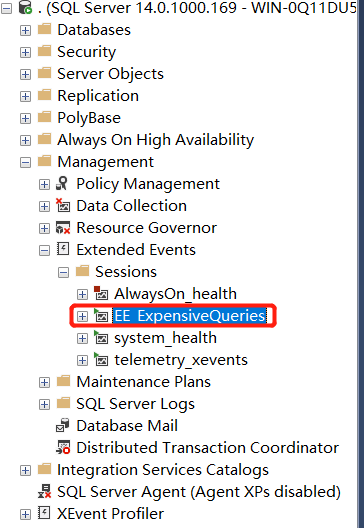 Extend Events Stored In UI Management
Extend Events Stored In UI Management
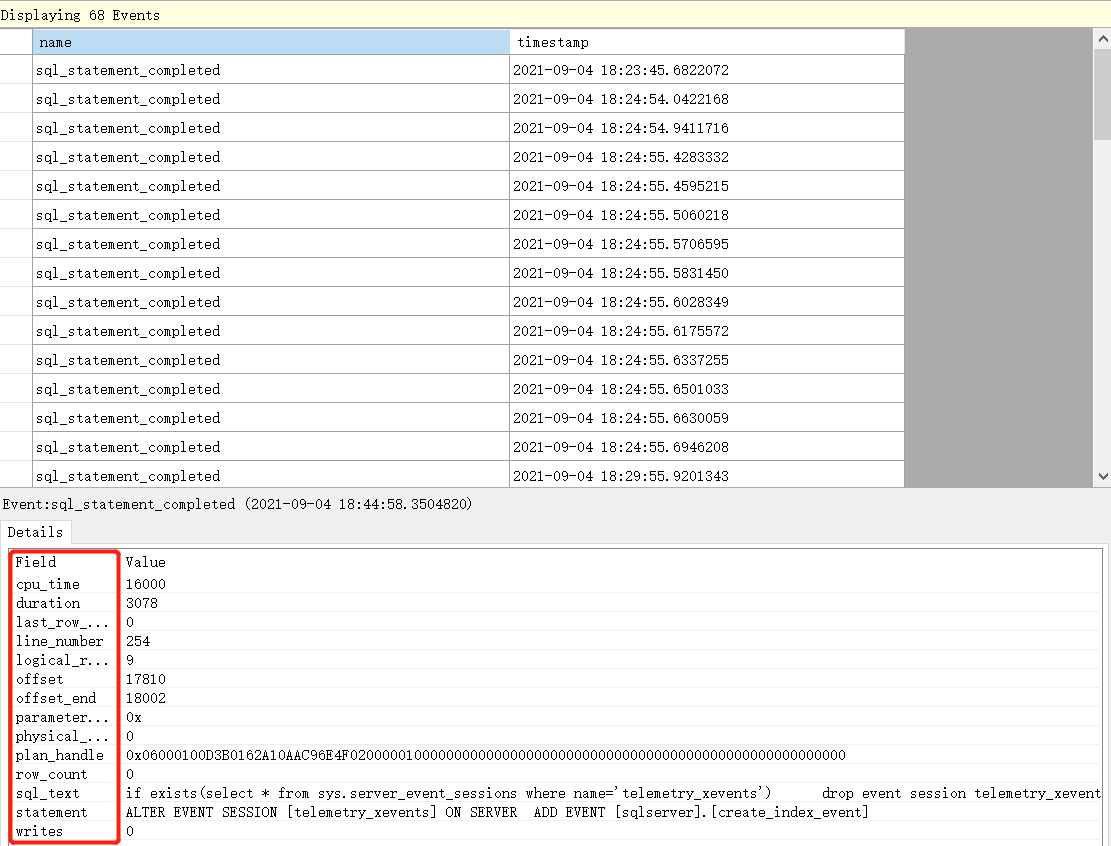 Management->Extended Events->Sessions
Management->Extended Events->Sessions
Query logs in SQL:
SELECT data FROM
(SELECT CONVERT (XML, event_data) AS data FROM sys.fn_xe_file_target_read_file
('C:\SQLskills\EE_ExpensiveQueries*.xel', 'C:\SQLskills\EE_ExpensiveQueries*.xem', NULL, NULL)
) entries;
GO
output:
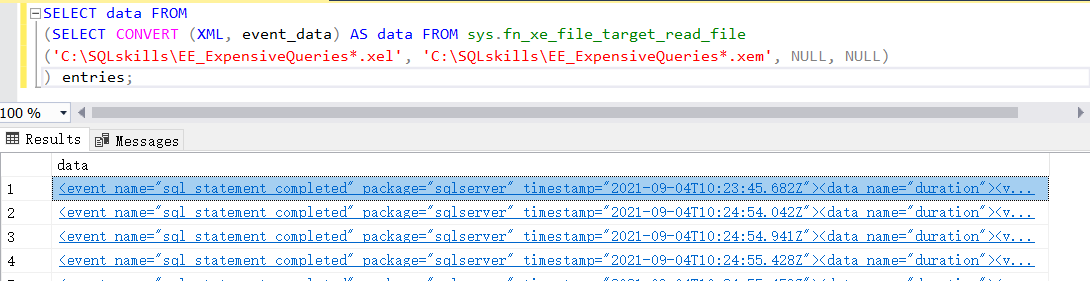 Query As XML format
Query As XML format

Comments