Docker Hub Automated Tests
16 Dec 2020 | Docker DevOpsIn the preceding article, we discussed the automated builds mechanism on the Docker Hub. And another cool feature of Docker Hub is the Automated Tests functionality.
Docker Hub enables you to build images from the source code, which needs to pass the tests. When you configured automated tests, the Docker Hub only builds the images when the tests passed. If an image failed on the tests, then it won’t be pushed into your docker hub registry.
It is easy to set up an automatic tests pipeline on Docker Hub.
Enable Automatic Tests on the docker hub dashboard
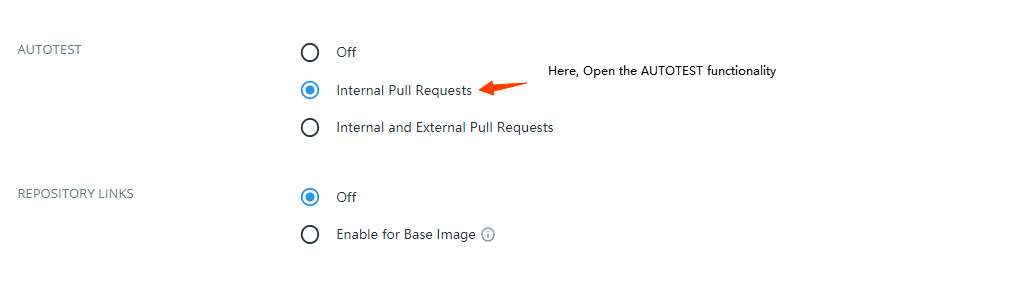 open automated test pipeline
open automated test pipeline
Set up automated test files
Docker Hub will identity files ending with .test.yml suffix as test files. If you specify more than one test file, the Docker Hub will run them sequentially.
The test file should look like this:
services:
sut:
build:
context: .
command: my_tests.sh
The my_tests.sh file returns 0 determines that the tests passed, and fail otherwise.
In the preceding article, I created a Github repository Docker Hub CI/CD Explanation for demonstration. Here, I am going to add automatic test files for that repository.
my project tests file architecture
├─tests
│ ├─unittest_api.py
│ └─unittest_module.py
├─docker-compose.test.yml
└─run_tests.sh
The docker-compose.test.yml is a test yaml file, which will be executed by the Docker Hub Tests pipeline. You can add more test yaml files, and they will be executed sequentially.
Let us take a look at my docker-compose.test.yaml file contents.
services:
sut:
build:
context: .
ports:
- "8000:8000"
command: run_tests.sh
The above snippet builds an image from the current directory and traffic the port to 8000 from 8000 inside the container. command: run_tests.sh means that running the run_tests.sh script after the image was build and the container was running up.
The image will be pushed into your docker hub registry, only when the tests passed.(aka the run_tests.sh returns code 0).
NOTE:In order to use
run_tests.shscript. You should make it executable and place it into the environment variables. Or specify the full executable file path in theservices.sut.command.Grant script executable and add it into environment variables with
ENVin Dockerfile.
Example:
RUN chmod +x /usr/src/app/run_tests.sh
ENV PATH="/usr/src/app"
The run_tests.sh is a simple Linux script, which was made to customize this demo project’s test for this article. You can change this script to fit your project’s tests.
In this example, the run_tests.sh file will execute all unit test files under the tests directory.
run_tests.sh contents:
#! /bin/bash
# run all unit test files that file name start with "unittest" under "test" dir.
for dir in $(ls tests -1FA | grep "^unittest");
do python3 tests/$dir;
done
I hope I made this article clear, and if there was something not clear, please be free to leave it in the comments.

Comments