Data Annotation - Timestamp Attribute
09 Apr 2020 | CSharp-EFTimestamp provides a mechanism that provides an increasing value. Do not cheat by its semantic. It doesn’t preserve any date or time. The Timestamp used as a synonym of rowversion. A Timestamp/rowversion is a property for which a new value will be generated automatically by the database every time a row is inserted or updated. The precise details of the implement are depending on the database provider.
The Timestamp/rowversion is also treated as a concurrency token, ensuring that you get an exception if a row you are updating has changed since you queried it.
For SQL server, a byte[] is usually used, which will be set up a rowversion column in the database.
public class Student
{
public int id { set; get; }
public string name { set; get; }
[Timestamp]
public byte[] token { set; get; }
}
sql server database screenshot.
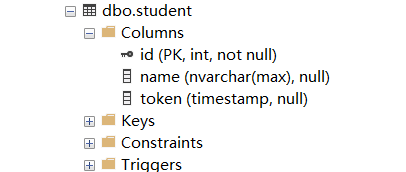
The token’s column data type is timestamp, which is the same thing with rowversion.
Now we are going to add some data for illustration.
using (var context = new SchoolContext()) {
//insert
context.Add<Student>(new Student() { name = "kobe" });
context.Add<Student>(new Student() { name = "curry" });
context.SaveChanges();
//query
Student kobe = context.student.Where<Student>(std => std.name.Equals("kobe")).FirstOrDefault();
//modify
kobe.name = "kobe bryant";
context.SaveChanges();
}
raw SQLs are below:
--insert data
exec sp_executesql N'SET NOCOUNT ON;
INSERT INTO [student] ([name])
VALUES (@p0);
SELECT [id], [token]
FROM [student]
WHERE @@ROWCOUNT = 1 AND [id] = scope_identity();
',N'@p0 nvarchar(4000)',@p0=N'kobe'
exec sp_executesql N'SET NOCOUNT ON;
INSERT INTO [student] ([name])
VALUES (@p0);
SELECT [id], [token]
FROM [student]
WHERE @@ROWCOUNT = 1 AND [id] = scope_identity();
',N'@p0 nvarchar(4000)',@p0=N'curry'
--query
SELECT TOP(1) [s].[id], [s].[name], [s].[token]
FROM [student] AS [s]
WHERE [s].[name] = N'kobe'
--update with token check
exec sp_executesql N'SET NOCOUNT ON;
UPDATE [student] SET [name] = @p0
WHERE [id] = @p1 AND [token] = @p2;
SELECT [token]
FROM [student]
WHERE @@ROWCOUNT = 1 AND [id] = @p1;
',N'@p1 int,@p0 nvarchar(4000),@p2 varbinary(8)',@p1=1,@p0=N'kobe bryant',@p2=0x00000000000007D1
As we can see from the raw SQLs. Each update or insert command has a select command on the end because EntityFramework needs to update its state.
The EntityFrameworkCore also will automatically apply the token check when the update occurred on tables that have a timestamp column applied. Just as the above illustration.

Comments