Parallel Processing In VBA
25 Jul 2021 | VBAHave you encountered the problem that you want to launch another thread to tackle other works when the current window is suspended(Such as, perform operations on the “Save As” window)? To be blunt, VBA doesn’t provide the multi-threads implementation.
VBA is a single-threaded translated scripting language. You cannot run multiple instances of VBA code in parallel.
Nonetheless, VBA doesn’t provide any available packages for multi-thread, But you can use the following alternative ways to achieve “multi-thread”.
- Using a C#.NET COM/dll
- VBscript worker threads
- VBA worker threads(via VBscript)
The following table illustrates their comparison, quoted from Analyst Cave’s blog Multithreading VBA – VBA vs. VBscript vs. C#.NET
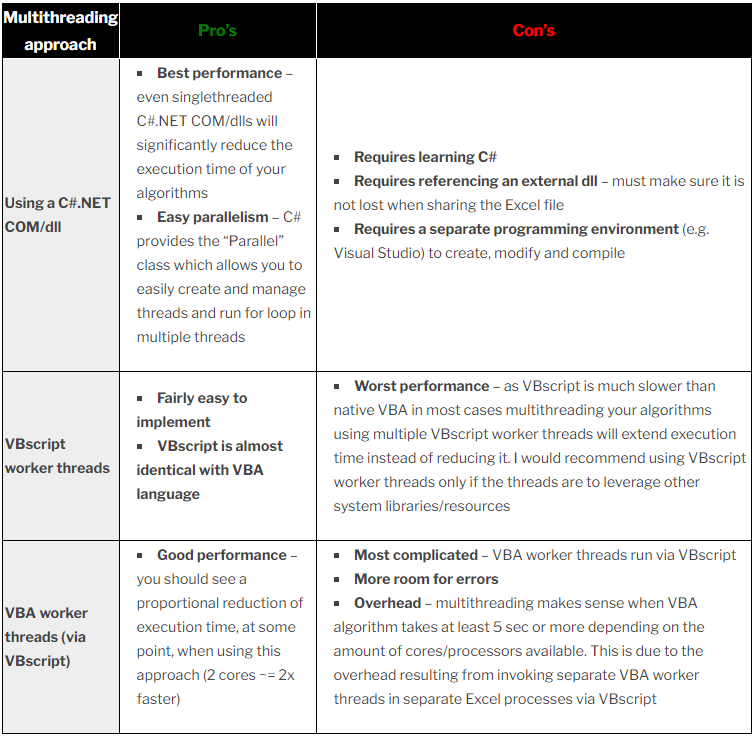 vba parallel processing’s method comparison
vba parallel processing’s method comparison
The above diagram compared their differences. I wouldn’t discuss VB Script and DLL in this article. The following snippet will illustrate the third solution, which is complicate and robutness.
Create an excel file and save it as an xlsm file, and open the VBA code editor.
MultiThreadHelper.xlsm
Sub Entry()
MsgBox "I come from another process"
End Sub
The above creates a simple snippet which gonna alert a message. You can implement your own logic.
Then Create another excel, which will going to invoke MultiThreadHelper’s Entry method asynchronously. In order to run MultiThreadHelper asynchronously, you should create a new excel application, instead of use the calling context. Otherwise, the invoking will be synchrounously.
Invoker.xlsm
Sub InvokeAsynchronously()
'invoke another excel file for paralle work
Dim helpFile As String
Dim objExcel
Set objExcel = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
objExcel.application.ScreenUpdating = True
' False, if you don't want make this excel visible
objExcel.application.Visible = True
objExcel.application.EnableEvents = True
helpFile = "'" & ThisWorkbook.Path & "\MultiThreadHelper.xlsm'!Entry"
'The current thread doesn't block at this method
'This method will be behavior asynchronously.
objExcel.application.Run helpFile
End Sub
As you noticed in the above snippet, InvokeAsynchronously creates another new Excel.Application object to run our MultiThreadHelper.xlsm file parallelly. The above snippet will launch another process that will gonna handle the MultiThreadHelper.xlsm’s running.
If you don’t want the MultiThreadHelper.xlsm being visible during execution, then you can hide it by setting objExcel.application.Visible to False.
The above snippet simply illustrated the idea of implementing a parallel in VBA. Next, I am gonna show you a more complicated scenario. In a VBA project, you are using UI Automation to operate a software, then you need to open a “Save As” window, and input the name, then trigger The “Save” button.
 save as button
save as button
With single thread VBA application, it’s almost impossible to operate the “Save As” Windows. The trick is that your VBA process gonna be suspended, once you open the “Save As” window. And your process resumes, when the “Save As” window closed. In order to input a name in the “Save As” window, you need to launch an assistive VBA process before current process’s suspendion, which is responsible for handling the “Save As” window.
MultiThreadHelper.xlsm
Option Explicit
Private Declare PtrSafe Function FindWindow Lib "user32" Alias "FindWindowA" (ByVal lpClassName As String, ByVal lpWindowName As String) As Long
Sub Entry(filename As String, times As Integer)
' if maximum times expired, then exist
If times <= 0 Then
Exit Sub
End If
Dim NewTime
NewTime = Now + TimeValue("00:00:03")
Debug.Print (NewTime)
' Check is if "Save As" opened
If FindWindow(vbNullString, "Save As") <> 0 Then
' Save As window opened, then do operation on VBA
' Input file name
' click "Save" button
Else
' Wait for 3 seconds, then run Entry method again !!!
Application.OnTime NewTime, "'Entry " & """" & filename & """ , " & (times - 1) & " '"
End If
End Sub
Invoker.xlsm
Sub InvokerTest()
CloseHelperWindowIfOpend()
LaunchAutoHelper()
' Open "Save As" window, then process suspend
' OpenSaveAsWindow()
' the process resume, once "Save As" window closed.
' do other operations
End Sub
Sub CloseHelperWindowIfOpened()
' Check is if MultiThreadHelper opened
If wbOpen("MultiThreadHelper.xlsm") = False Then
Exit Sub
End If
' Close opened window
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open(ThisWorkbook.Path & "\MultiThreadHelper.xlsm")
wb.Save
wb.Close False
End Sub
Sub LaunchAutoHelper(filename As String)
'invoke another excel file for parallel work
Dim helpFile As String
Dim objExcel
Set objExcel = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
objExcel.application.ScreenUpdating = True
' makes window hidden during execution
objExcel.application.Visible = False
objExcel.application.EnableEvents = True
helpFile = "'" & ThisWorkbook.Path & "\MultiThreadHelper.xlsm'!Entry"
' objExcel.application.Run helpFile, filename
' waiting for 60*3 = 180s
objExcel.application.Run helpFile, filename, 60
End Sub
The above example demonstrated a common usage, that you propably gonna meet while you are handling with a “Save As” or “Open” window. As I mentioned early, there are three available methods that you can make capital with, when you are tackling the parallelization work in VBA. But I prefer the VBA Excel method, the following lists several adavantages compared to others.
- Stable performance
- Convenient for managing source code
- Convenient for debuging

Comments